What Are the Fundamental Steps to Write a Dissertation?
What is a Dissertation?
A dissertation, also known as a thesis in some countries, is a long piece of academic writing based on original research. It is typically submitted as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. A dissertation can vary greatly in length depending on the degree level and the specific field of study. For example, a PhD dissertation may be upwards of 100 pages, while an undergraduate dissertation is generally shorter.
The purpose of a dissertation is to demonstrate a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to existing scholarly work. It involves identifying areas for research, developing original questions, and making a significant contribution to the academic discipline. The two key types of dissertations include primary research or secondary research, such as library-based dissertation.
Ace Your Dissertation with Expert Guidance!
Struggling with your dissertation? Elite Thesis Help provides expert guidance, customised support, and research solutions to ensure you succeed. Don’t let stress hold you back—partner with our experts and make your academic goals a reality today!
What Are the 9-Step Guides for Writing a Dissertation?
Writing a dissertation can be one of the most challenging but rewarding parts of your academic journey. Whether you are at the undergraduate level, pursuing a master’s degree, or even a doctoral candidate, completing a dissertation is an essential milestone. It requires original research and is often the most substantial piece of academic work you will undertake during your studies.
This guide will cover essential steps for writing a successful dissertation, from choosing a research topic to structuring the final document effectively. Let’s break down each step to help you navigate this important academic requirement smoothly.

The dissertation process can be daunting, especially if you’re starting your dissertation journey without a clear idea of the stages involved. Below are the essential steps to successfully complete your dissertation:
- Choose a Research Topic: Selecting the right research topic is crucial. It must be a subject that interests you and has enough existing research to support your work. This topic will drive the entire dissertation process, so it’s a good idea to discuss it with your supervisor.
- Write a Dissertation Proposal: A dissertation proposal serves as a roadmap for your research. It outlines your research question, methodology, and the scope of your work. Proposals are critical as they allow supervisors to understand your aims and provide feedback.
- Conduct a Literature Review: A literature review involves summarising existing research related to your topic. This helps identify gaps in the literature and situates your work within the broader field of study.
- Develop Your Methodology: The methodology chapter outlines how you will conduct research, including data collection and analysis techniques. This section must be clear and justify your chosen approach.
- Conduct Original Research: Depending on your field, you may need to conduct experiments, surveys, or interviews to gather data. This step is often the most time-consuming, especially for graduate students or doctoral candidates conducting complex studies.
- Analyse Your Findings: Once you collect your data, analysing the findings is key to producing original contributions to your field. Use appropriate analysis methods and explain your results in detail.
- Write Your Dissertation: Begin to write your dissertation, following a structured format. It should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology chapter, results, a discussion, and a conclusion.
- Edit and Revise: Writing a dissertation is an iterative process. Draft your chapters, review them, and revise as necessary. Pay attention to feedback from your supervisor and be prepared to make changes.
- Submit and Defend: After completing the written part, you will often need to defend your dissertation before a committee. This oral examination is your opportunity to present your research and respond to questions.
How to Choose a Topic for Your Dissertation?
Choosing a topic can be one of the hardest parts of starting your dissertation. Your research topic should be something that interests you and contributes to your field of study. It should be specific enough to allow for in-depth study but broad enough to have ample existing research literature to build upon. It’s a good idea to speak with your supervisor or consult subject guides available through your university.
Here are some tips to help you choose a suitable dissertation topic:
- Identify Your Interests: Start by listing topics that genuinely interest you. A dissertation is a long process, and staying motivated is easier if you are passionate about your subject.
- Assess the Scope: Ensure that your topic is not too broad or too narrow. A broad topic may be overwhelming, while a very narrow topic may lack sufficient research material. Finding the right balance is key.
- Review Existing Literature: Look at existing research literature to understand what has already been studied and where there might be gaps. This will help you identify areas where you can make an original contribution.
- Consider Relevance and Contribution: Choose a topic that is relevant to your field of study and has the potential to make a meaningful contribution. Your dissertation should aim to fill a gap in the existing research or provide new insights.
- Discuss with Your Supervisor: Your supervisor can provide valuable feedback and guidance on your chosen topic. They can help you refine your research question and ensure that it is feasible within the scope of your degree program.
- Check Feasibility: Consider practical aspects such as data availability, time constraints, and resource requirements. Make sure your topic is feasible given the resources you have at your disposal.
- Be Open to Adjustments: Your initial topic may evolve as you delve deeper into your research. Be flexible and willing to refine your focus as you gather more information and insights.
Choosing the right topic, such as in the paramedics research, is a crucial first step in your dissertation journey. A well-chosen topic will provide a strong foundation for your research and help ensure that your dissertation is both manageable and impactful.
What Is the Importance of a Dissertation Proposal?
A dissertation proposal is an important document in the dissertation process. It defines your research question, outlines the methodology, and sets the stage for your project. This proposal must be approved by your supervisor or academic committee, making it essential to communicate your ideas clearly and concisely. The proposal is not only a formal requirement but also a planning tool to keep you focused throughout the dissertation process.
The importance of a dissertation proposal can be summarised as follows:
- Clarifies Your Research Direction: The proposal helps you clarify your research direction and ensures that you have a clear understanding of what you want to achieve. It serves as a roadmap, guiding you through the research process.
- Provides Structure: A well-structured proposal includes your research question, objectives, literature review, methodology, and timeline. This structure helps you plan your work and ensures that all aspects of the research are considered before you begin.
- Facilitates Supervisor Feedback: The proposal is an opportunity to get feedback from your supervisor before you start the main research. Their input can help you refine your research question, improve your methodology, and avoid potential pitfalls.
- Demonstrates Feasibility: Your proposal must show that your research is feasible within the given timeframe and with the resources available. It forces you to think about practical issues such as data collection, analysis methods, and potential challenges.
- Secures Approval: Most academic programs require the proposal to be approved before you can proceed. This approval process ensures that your research meets academic standards and is viable in terms of scope and methodology.
- Keeps You Focused: Writing a dissertation can be a lengthy process, and it’s easy to lose focus. A proposal acts as a reference point, helping you stay on track and reminding you of your original aims and objectives.
- Identifies Potential Challenges: Developing a proposal allows you to anticipate potential challenges and plan accordingly. By thinking through the research process in advance, you can identify areas that may require additional resources or adjustments.
How to Structure Your Dissertation Effectively?
To write a successful dissertation, structuring it effectively is crucial. Most dissertations follow a typical structure, which includes the following sections:
The importance of a dissertation proposal can be summarised as follows:
- Title Page: Includes your dissertation title, your name, degree, and institution.
- Abstract: A short summary of the entire dissertation, usually no more than 300 words long.
- Table of Contents: Lists all the sections and chapters, along with page numbers.
- Introduction: Sets out the research topic, research questions, and objectives.
- Literature Review: Summarises existing research and identifies gaps that your work addresses.
- Methodology: Describes the research methods, tools, and data collection techniques used.
- Results: Presents the findings of your research in detail.
- Discussion: Analyses the results and explains their implications.
- Conclusion: Summarises the main points and highlights the significance of your findings.
- References/Bibliography: Lists all the works cited in your dissertation.
Effective structuring ensures your dissertation flows logically and meets the expectations of your academic discipline.
Unlock Dissertation Success Effortlessly!
Take the stress out of dissertation writing with Elite Thesis Help. Our experienced experts are ready to provide the tailored support you need—from drafting to editing. Start your journey towards academic success now, and let’s make your dissertation stand out!
How to Conduct a Literature Review for Your Dissertation?
A literature review is an essential part of a dissertation or thesis, especially for advanced degrees such as master’s or doctoral programs. It provides a comprehensive overview of the research literature related to your topic, summarising existing studies and highlighting gaps that your work aims to fill. Conducting a literature review helps you build a solid foundation for your project, ensuring that your research is grounded in established knowledge and contributing something new to the academic discipline.
Here is a step-by-step guide to conducting a literature review:
- Define Your Scope: Before you begin, determine the scope of your literature review. This will depend on your field of study and the requirements set by your institution. For instance, the word count and depth of a literature review for an undergraduate studies dissertation will differ from that of a doctoral dissertation.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use academic databases to find relevant sources. Look for scholarly articles, books, and doctoral dissertations that are related to your research question. U.S. university libraries often provide access to extensive databases, making it easier to find high-quality sources.
- Organise Your Sources: As you find relevant sources, organise them by themes or key topics. This will help you see how different studies are connected and identify common themes or debates. Many dissertations are structured around thematic organisation, which can make the writing process more coherent.
- Summarise and Synthesise: Summarise the key findings of each source and synthesise them to show how they relate to each other. It is important to follow a systematic approach, ensuring that your review is not just a collection of summaries but a cohesive piece of writing that provides insights into the research literature.
- Identify Gaps in the Literature: One of the key purposes of the literature review is to identify gaps in existing research. By pinpointing areas that have not been thoroughly studied, you can justify the need for your own research project.
- Write the Review: Once you have gathered and organised your sources, write the literature review. Include an introduction and conclusion to frame your discussion, and ensure that the content is coherent and logically structured. The introduction should provide context, while the conclusion should summarise the key themes and highlight the research gaps your dissertation aims to address.
What to Include in Your Literature Review?
When writing a literature review, it is important to include certain elements to ensure it meets academic standards. Here’s what to include in your literature review:
- Introduction: The introduction should set the stage for your literature review. It should provide a short summary of your research topic, explaining its importance and relevance. The introduction must also outline the scope of the review and the key themes that will be covered.
- Thematic Organisation: Your literature review should be organised thematically, methodologically, or chronologically, depending on what best suits your topic. This helps you present a coherent picture of the current state of knowledge in your field.
- Critical Analysis: It is not enough to merely summarise the existing research; you should critically analyse it. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of different studies, and explain how they contribute to or fall short of addressing your research question.
- Gaps in the Research: Identify any gaps in the research literature. These gaps represent opportunities for your dissertation to make an original contribution. Highlighting these gaps helps justify your research project and its significance.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarise the key findings from the literature and point out the direction your research will take. It should concisely restate why your research is needed and how it will address gaps in the existing body of work.
A well-structured literature review not only provides a foundation for your research but also positions your work within the larger academic conversation.
How to Analyse Sources for Your Research Project?
Analysing sources is a critical component of the literature review and overall research process. To effectively analyse your sources, follow these steps:
- Evaluate Credibility: Assess the credibility of each source. Peer-reviewed journals and academic books are generally reliable, while other types of publications may require more scrutiny. Look at the author’s credentials, the publication venue, and the reference style used to gauge reliability.
- Identify Key Arguments: Determine the main arguments and findings presented in each source. Summarise these key points, noting how they relate to your research topic. This step will help you understand the broader conversation happening in your field and how your work fits into it.
- Assess Methodology: Evaluate the methodology used in each study. Is the research design sound? Are the data collection and analysis methods appropriate? Identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the methodologies will help you build a critical perspective on the literature.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare different sources to identify similarities, differences, and patterns in the findings. This comparative analysis is key to synthesising information and creating a cohesive literature review.
- Contextualise the Findings: Place each source within the context of your research question. Determine how each source contributes to answering your research question or identifying gaps. This will make it easier to construct a narrative that supports the rationale for your dissertation.
- Use Direct Quotations Sparingly: While quoting can be helpful, use direct quotations sparingly. It is often better to paraphrase and summarise to demonstrate your understanding of the material. Make sure to provide proper citations, adhering to the reference style required by your institution.
Analysing sources thoroughly ensures that your literature review is not just descriptive but also critical and insightful. This depth of analysis is what differentiates undergraduate and masters level dissertations from doctoral dissertations, where deeper engagement with the research literature is expected.
What Are Common Mistakes in Writing a Literature Review?
Writing a literature review can be challenging, and there are several common mistakes that students typically make, including the radiography dissertation writing process. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and write a more effective literature review:
- Lack of a Clear Focus: One of the most common mistakes is failing to provide a clear focus or research question. A literature review should not be a random collection of sources but rather a structured piece of writing that addresses specific themes or questions. Make sure that your review is centred around your research aims.
- Descriptive Rather than Analytical: Many students fall into the trap of merely summarising sources without providing critical analysis. Your literature review should go beyond description; it should assess the validity, reliability, and contribution of each study to the field. Analytical depth is especially important for doctoral programs and advanced degrees.
- Poor Organisation: A literature review must be well-organised to be effective. Disorganised reviews can confuse the reader and obscure the main points. To avoid this, follow a clear structure, such as thematic, chronological, or methodological organisation. This will help you create a logical flow and connect different studies coherently.
- Ignoring Gaps in the Research: Failing to identify gaps in the research literature is a critical mistake. Identifying gaps is key to justifying your research, as it shows how your dissertation contributes to the field. Always highlight what is missing in the literature and how your project aims to fill those gaps.
- Inadequate Referencing: Improper or inconsistent referencing is another common mistake. Make sure to use the reference style required by your institution and be consistent throughout. Proper referencing not only gives credit to original authors but also adds credibility to your work.
- Overuse of Direct Quotes: Using too many direct quotes can make your literature review look like a compilation of other people’s work rather than your own analysis. Instead, summarise or paraphrase when possible, and use direct quotes only when the wording is particularly impactful or significant.
- Ignoring Module Guidelines: Each institution has its own guidelines for writing a literature review, including word count and assessment criteria. It is important to follow these guidelines closely to ensure that your review meets the academic standards required for your program.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your literature review is a strong foundation for your dissertation, providing a clear rationale for your research and demonstrating your ability to engage critically with existing scholarly work.
What Should Be Included in the Dissertation Format?
The dissertation format is a critical component of the overall project. It provides a clear and structured way to present your research, making it easier for the reader to follow your argument and understand your findings. The format of your dissertation will depend on your institution’s requirements, but there are standard elements that should be included regardless of the specific guidelines you are following.
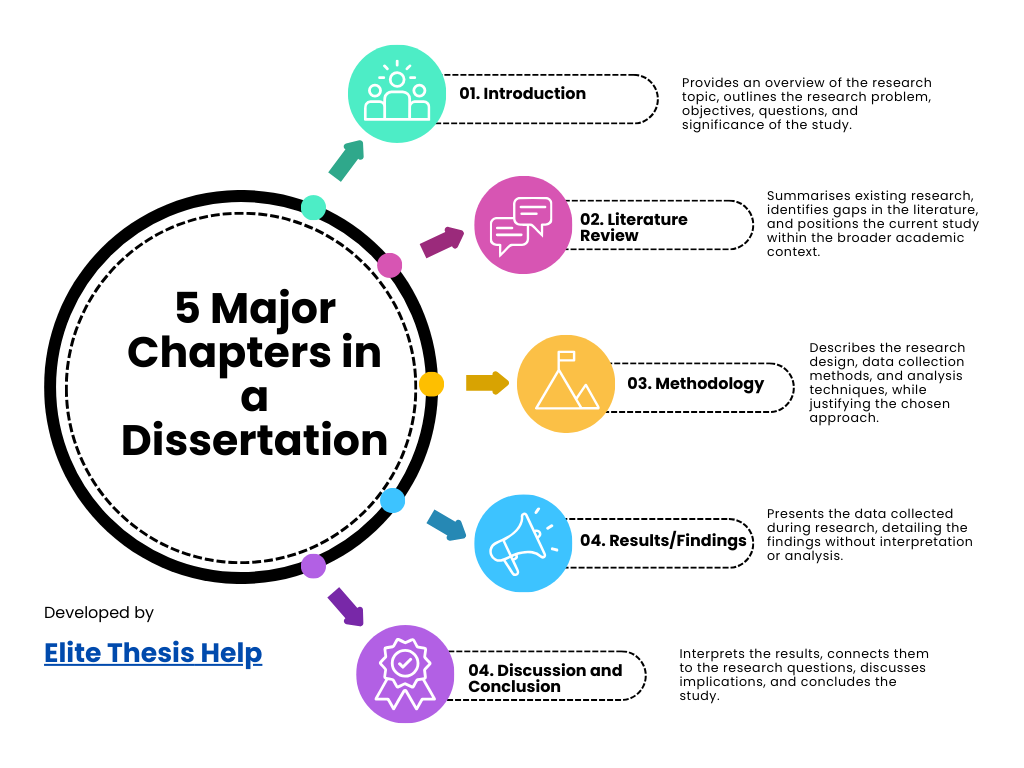
Here is a detailed outline of what should be included in the dissertation format:
- Title Page: The title page is the first page of your dissertation and includes key information such as the title of your dissertation, your name, the degree for which you are submitting the dissertation, your institution, and the submission date. Creating a clear and informative title page is important as it provides the reader with an initial understanding of the focus of your research.
- Abstract: The abstract is a short summary of the entire dissertation, typically between 150 and 300 words long. It provides an overview of the research question, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be concise yet informative, giving the reader a snapshot of what to expect in the dissertation.
- Table of Contents: The table of contents lists all the chapters and major sections of your dissertation along with their page numbers. This helps the reader navigate the document and locate specific information easily. The role of the table of contents is crucial, especially in a long piece of writing, as it ensures that your dissertation is well-organised and easy to follow.
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your dissertation. It introduces the research topic, explains the background, and states the research question and objectives. The introduction should also outline the structure of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of what to expect in each chapter.
- Literature Review: The literature review summarises and analyses existing research related to your topic. It highlights gaps in the literature that your research aims to fill and establishes the theoretical foundation for your study. This section is important to show that your work is grounded in existing scholarly research and contributes new insights.
- Methodology: The methodology chapter explains how you conducted your research. It includes details on the research design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. The methodology should be detailed enough to allow another researcher to replicate your study if desired.
- Results: The results chapter presents the findings of your research. It may involve statistical analyses, tables, and figures to present the data clearly. This section is strictly about presenting the findings without interpretation.
- Discussion: The discussion chapter interprets the results, explaining their significance and how they relate to your research question. This section should link your findings to the existing research discussed in your literature review and provide insights into the implications of your study.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarises the main findings of your research, discusses their significance, and suggests areas for future research. The conclusion should be concise and bring closure to the dissertation by restating the key contributions of your work.
- References/Bibliography: The references section lists all the sources cited in your dissertation. It is important to follow the reference style required by your institution, whether it is APA, MLA, Chicago, or another format. Proper referencing gives credit to the original authors and helps avoid plagiarism.
- Appendices: Appendices may include supplementary material such as raw data, questionnaires, or additional tables. Including appendices helps keep the main text focused while providing additional information for readers who are interested in the details.
Your Dissertation Journey Made Simple!
Stuck with your dissertation? Elite Thesis Help makes it simple with step-by-step support. From planning to writing, we’re here to help you excel. Get started now and watch your academic dreams take shape—achieve more with Elite Thesis Help!
How to Create a Title Page for Your Dissertation?
The title page is a critical part of your dissertation as it provides the first impression of your work. Creating an effective title page involves including all the necessary information in a clear and organised manner. Here are the key elements to include on your title page:
- Dissertation Title: The title should be descriptive and reflect the focus of your research. It should be specific enough to give the reader an idea of the content but not overly long or complex.
- Author’s Name: Include your full name as it appears in the university records.
- Degree Program: State the degree for which the dissertation is submitted, e.g., “Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in [Subject].”
- Institution Name: Include the full name of your university or institution.
- Submission Date: Provide the month and year of submission.
- Supervisor’s Name (optional): Some institutions may require you to include the name of your dissertation supervisor.
The title page should be formatted according to your institution’s guidelines. It is typically the first page of the dissertation but does not have a page number.
What Is the Role of the Table of Contents?
The table of contents (TOC) is an essential part of your dissertation, serving as a roadmap for the reader. It lists all the major sections and subsections of your dissertation, along with their corresponding page numbers. The role of the table of contents is to provide structure and help the reader navigate through the document.
A well-organised TOC should include:
- Main Chapters: List all the main chapters, such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion.
- Subsections: Include any major subsections within each chapter to give the reader a detailed view of the content.
- Page Numbers: Ensure that the page numbers listed in the TOC match the actual pages in the document.
The TOC should be updated throughout the writing process to reflect any changes in the structure of the dissertation. Most word processing software, such as Microsoft Word, provides tools to automatically generate and update the table of contents, which can be helpful in maintaining accuracy.
How to Write an Effective Thesis Statement?
The thesis statement is a crucial component of your dissertation’s introduction. It provides a concise summary of the main point or argument of your dissertation. An effective thesis statement should be clear, specific, and arguable, providing a focus for your research and guiding the direction of your study.
Here are some tips for writing an effective thesis statement:
- Be Specific: Your thesis statement should be specific and indicate precisely what your dissertation will cover. Avoid vague or broad statements that do not convey the central focus of your work.
- Make It Arguable: A strong thesis statement should present a claim or argument that others could potentially dispute. This makes your research more engaging and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Place It Early: The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your introduction, giving the reader a clear idea of your research focus from the beginning.
- Reflect Your Research Question: The thesis statement should reflect your research question and indicate how you plan to address it. It serves as a summary of your research objectives and the contribution your dissertation will make to the field.
- Revise as Needed: As you progress through your research, you may need to revise your thesis statement to better reflect your findings and conclusions. It is important that the thesis statement remains aligned with the content of your dissertation.
An effective thesis statement is the foundation of a successful dissertation, providing clarity and direction for both the writer and the reader. It sets the tone for your research and helps ensure that your dissertation stays focused and coherent.
What Are the Differences Between Undergraduate and Postgraduate Dissertations?
The differences between undergraduate and postgraduate dissertations primarily lie in their complexity, depth, and expectations. Both types of dissertations require independent research, but the level of detail and the scope of the research vary significantly.
- Complexity and Depth: An undergraduate dissertation is generally less complex compared to a postgraduate dissertation. Undergraduate dissertations are often descriptive and may involve summarising existing research rather than generating new insights. In contrast, postgraduate dissertations, such as those at the master’s or doctoral level, are expected to contribute original findings to the field. The complexity of the research question and the depth of analysis are much greater in postgraduate work.
- Length: The length of a dissertation depends on your field of study and the degree level. Undergraduate dissertations are typically shorter, often ranging from 8,000 to 12,000 words, while master’s level dissertations can range from 15,000 to 20,000 words. Doctoral dissertations are the longest, often exceeding 50,000 words. The word count is often specified by the institution, and students are required to write within these limits.
- Original Contribution: In undergraduate dissertations, students are often not required to make an original contribution to the field. The focus is on demonstrating an understanding of the subject and the ability to conduct independent research. Postgraduate dissertations, particularly at the doctoral level, require students to make a significant original contribution. This involves identifying gaps in the existing literature and providing findings in response to those gaps.
- Research Scope: The scope of research is another key difference. Undergraduate dissertations often focus on a narrow topic, and the research may be limited in terms of data collection and analysis. Postgraduate dissertations, on the other hand, involve broader and more in-depth research, requiring comprehensive data collection and rigorous analysis. For example, in science subjects, postgraduate dissertations may involve complex experiments and data analysis, while undergraduate dissertations may be more limited in scope.
- Supervisor Guidance: Undergraduate students receive more guidance and support from their supervisors compared to postgraduate students. At the master’s and doctoral levels, students are expected to take more initiative in designing their research and managing the dissertation process.
- Dissertation Defense: In many postgraduate programs, students are required to defend their dissertation in an oral examination. This dissertation defense involves presenting the research to a committee and responding to their questions. Undergraduate dissertations typically do not require a formal defense, although some programs may have a presentation component.
How Length of a Dissertation Varies by Degree Level?
The length of a dissertation varies significantly by degree level. As mentioned earlier, the word count is often specified by the institution and depends on the field of study. Here is a general overview of how dissertation length varies:
- Undergraduate Dissertations: Typically range from 8,000 to 12,000 words. These dissertations are usually completed in the final year of undergraduate studies and serve as a capstone project that summarises the student’s learning and research skills.
- Master’s Level Dissertations: Usually range from 15,000 to 20,000 words. At this level, students are expected to provide a more detailed analysis and demonstrate a deeper understanding of their research topic. The length also allows for more comprehensive literature reviews and data analysis.
- Doctoral Dissertations: Often exceed 50,000 words and can be much longer depending on the field. Doctoral candidates are required to make an original contribution to their field, which often involves extensive data collection, analysis, and a detailed discussion of the findings.
The length of the dissertation depends on the subject and the specific requirements set by the institution. For example, dissertations in science subjects may involve a shorter word count but require more experimental data, while dissertations in humanities may be longer due to the extensive analysis of literature and theories.
What Are Key Elements of a Successful Dissertation?
A successful dissertation includes several key elements that contribute to its quality and impact. These elements ensure that the dissertation is well-structured, coherent, and meets academic standards:
- Clear Research Question: A successful dissertation starts with a well-defined research question. The question should be specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study. It provides direction for the research and helps maintain a clear focus throughout the dissertation.
- Comprehensive Literature Review: The literature review should provide a thorough overview of existing research related to the topic. It should identify gaps in the literature and establish the theoretical foundation for the study.
- Methodological Rigor: The methodology should be well-designed and appropriate for the research question. It should include details on data collection, analysis techniques, and any limitations. The methodology section should be detailed enough to allow replication of the study.
- Critical Analysis: A successful dissertation goes beyond describing the research findings. It provides critical analysis, interpreting the results in relation to the research question and existing literature. This analysis should highlight the significance of the findings and their implications for the field.
- Coherent Structure: The dissertation should be well-structured, with a logical flow from one section to the next. Each chapter should build on the previous one, leading to a cohesive argument that supports the research question.
- Original Contribution: At the postgraduate level, a key element of a successful dissertation is its original contribution to the field. The research should add new insights, address gaps in the literature, or provide a novel perspective on an existing issue.
- Proper Referencing: Proper referencing is essential to avoid plagiarism and give credit to original authors. The dissertation should follow the required reference style and include all sources cited in the text.
Get Professional Dissertation Help Today!
Need help tackling your dissertation? Elite Thesis Help offers tailored support from topic selection to final submission. Secure your success with our professional guidance and make dissertation writing a stress-free journey. Get in touch and boost your grades!
How Does Writing a Thesis Differ from Writing a Dissertation?
The terms “thesis” and “dissertation” are often used interchangeably, but there are key differences between the two, particularly in terms of academic level and purpose:
- Academic Level: In many countries, a thesis is associated with a master’s degree, while a dissertation is associated with a doctoral degree. For example, in the U.S., a master’s student is required to write a thesis, while a doctoral candidate is required to write a dissertation. In contrast, in some countries, the terms are used differently, with a thesis referring to the final project submitted for a bachelor’s degree and a dissertation for a master’s or doctoral degree.
- Purpose: A thesis is typically a shorter piece of work that demonstrates the student’s understanding of existing research and their ability to analyse and synthesise information. It often involves responding to a specific research question by summarising existing literature and providing some original analysis. A dissertation, on the other hand, is a longer and more in-depth piece of research that involves making an original contribution to the field. The dissertation writing process includes identifying gaps in the literature, conducting original research, and presenting new findings.
- Length and Scope: A thesis is generally shorter than a dissertation. A master’s thesis may range from 10,000 to 20,000 words, while a doctoral dissertation can exceed 50,000 words. The scope of a dissertation is also broader, involving more comprehensive research and a higher level of analysis.
- Research Focus: A thesis is often focused on a specific question and involves summarising and synthesising existing research. In contrast, a dissertation involves a more complex research question and requires original data collection and analysis. The dissertation aims to address a gap in the literature and make a significant contribution to the academic field.
- Defense Requirement: In many postgraduate programs, students are required to defend their dissertation in an oral examination. This involves presenting the research to a committee and answering questions. A thesis defense is less common, although some programs may require students to present their findings.
Understanding these differences is important for students as they prepare for their academic journey. Whether you are writing a thesis or a dissertation, both require careful planning, rigorous research, and effective writing to produce a high-quality final product.
FAQs about Dissertation
How long is a full dissertation?
The length of a full dissertation varies depending on the academic level and institution. A master’s dissertation usually ranges from 15,000 to 20,000 words, while a PhD dissertation might be between 80,000 and 100,000 words. Dissertation examples illustrate that the topic is often chosen by the student in response to a question or hypothesis, requiring detailed research over an extended period.
How hard is it to get a 2:1 in a dissertation?
Achieving a 2:1 in a dissertation can be challenging due to the required time and word count, and the depth of analysis needed. Success depends on effectively selecting a topic, conducting thorough research, and structuring the response to a question well. Dissertation examples show that meeting expectations for critical analysis and originality is crucial for attaining a 2:1 grade.
Is 5000 words a dissertation?
A 5000-word document is usually not considered a full dissertation but could be an extended essay or a research project. Dissertation examples generally have a higher word count, e.g., around 10,000 words for an undergraduate level or 15,000 to 80,000 for graduate studies. A dissertation comes with the expectation of detailed research and analysis chosen by the student in response to a question, which typically requires more extensive writing.
What are examples of dissertations?
Dissertation examples often cover diverse topics, chosen by the student in response to a question within their field of study, e.g., an investigation into the impact of climate policy. Dissertations come in different formats, such as literature reviews, case studies, or empirical research. The aim is to answer a question or provide insight into an issue, demanding significant time and word count to explore the topic comprehensively.
