What is Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Research?
- Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyse, and report patterns (themes) within data.
- It allows qualitative researchers to interpret aspects of the data set and makes sense of complex, rich data, whether from interviews, focus groups, or text data.
- In qualitative data analysis, thematic analysis focuses on the themes that emerge within the data and provides an organised way of analysing these themes.
Understanding the Basics of Thematic Analysis
- Thematic analysis involves searching for and identifying recurring patterns or themes across a dataset.
- The process typically includes data collection, followed by coding the data into themes or categories.
- Researchers will use thematic analysis to code qualitative data, creating a system where these codes are grouped into broader categories representing important patterns.
- The research question often guides the themes being searched for in the data, providing a clear focus during the analysis of qualitative information.
- This method allows the researcher to highlight key themes relevant to the research question, allowing insights that speak to the research objectives.
Get Expert Help with Your Dissertation
Struggling with your dissertation? Let Elite Thesis Help provide expert writing services to ensure your research stands out. Get personalised assistance and top-quality work. Contact us now for your academic success.
Importance of Thematic Analysis in Qualitative Data
- Thematic analysis offers a flexible approach for qualitative researchers to conduct a qualitative analysis, as it can be applied across a variety of disciplines.
- In fields like psychology, thematic analysis is especially useful, such as thematic analysis in psychology, where researchers analyse participants’ responses or behaviours to explore underlying psychological processes.
- Thematic analysis makes it easier for researchers to distill qualitative research in psychology into themes, making complex data more accessible and actionable.
- It enables researchers to focus on significant themes and insights that emerge within the data, leading to conclusions that are deeply grounded in the participants’ experiences.
How Does Thematic Analysis Differ from Other Qualitative Research Methods?
- While other qualitative methods, like content analysis, focus on categorising data into predefined themes, thematic analysis is more flexible, allowing for the search for themes that emerge from the data without predetermined categories.
- Discourse analysis focuses on how language shapes meaning within a context, whereas thematic analysis looks at recurring themes across qualitative data.
- Thematic analysis is also distinguished from other methods like data collection techniques such as interviews, surveys, and focus groups, as it provides a methodical approach to analyze the data and identify patterns of meaning within a dataset.
How to Conduct a Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a widely used method of analysis in qualitative research, allowing researchers to identify, analyse, and interpret patterns (themes) within qualitative data. Below is a step-by-step guide to conducting thematic analysis effectively.
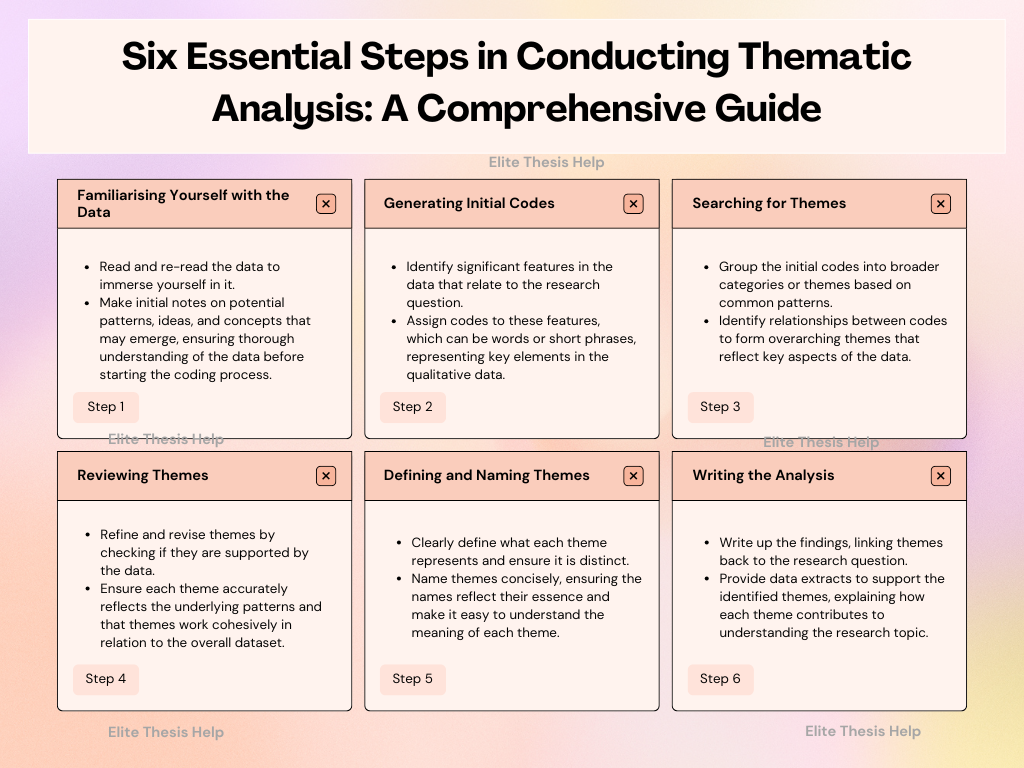
Step-by-Step Process of Thematic Analysis (6 Steps)
- Step 1: Data Familiarisation
- Begin by reading through your transcription of data multiple times. This ensures you are familiar with the content before starting any analysis of the data.
- Making sense of qualitative data at this stage will allow you to identify potential themes that may emerge.
- Step 2: Generating Initial Codes
- The process of coding involves breaking down the data into smaller chunks of information. You can do this manually or using qualitative data analysis software.
- The coding is the process of categorising and labelling these chunks of data in relation to your research question.
- Step 3: Searching for Themes
- Once you have initial codes, group them into potential themes and patterns. At this point, you can begin to create a thematic map to visualise the relationships between the codes.
- Thematic analysis provides a way to explore the relationship between different data points, which can give more insight into the data in relation to the research question.
- Step 4: Reviewing Themes
- Review the identified themes to ensure they accurately reflect the data. The thematic analysis process includes rechecking whether each theme is sufficiently supported by the data.
- Interpretation of the data helps refine and finalise these themes, ensuring their relevance and coherence.
- Step 5: Defining and Naming Themes
- Clearly define each theme and provide a concise label. This is where interpretive analysis comes in to ensure that each theme is understood in the context of the research.
- Themes and patterns should reflect the core meaning of the data, so clarity is important when naming them.
- Step 6: Writing Up the Thematic Analysis
- In the final step, write up the thematic analysis of qualitative data, providing detailed descriptions of the themes and how they relate to the research data.
- Include coding your qualitative data and how each theme connects to the research questions, offering insights gained through the analysis helps approach.
Key Techniques for Effective Thematic Analysis
- Use of Qualitative Content Analysis: A qualitative content analysis approach can be used to complement thematic analysis. This provides a structured method of examining textual data and allows for deeper insights into patterns.
- Coding and Categorising Data: Coding is a crucial technique in the thematic analysis process. A coding manual for qualitative researchers can help standardise the process and ensure consistency throughout the analysis.
- Inductive and Deductive Analysis: Inductive analysis is based on letting themes emerge from the data, while deductive thematic analysis uses predefined theories to guide the search for themes.
Common Mistakes in Conducting Thematic Analysis
- Over-coding: Over-coding can lead to fragmented data, making it difficult to understand the broader themes. Ensure that coding is focused on meaningful categories.
- Not Considering Context: When performing analysis of the data, it’s important not just to code individual words or phrases but to consider the broader context, which can significantly impact the interpretation.
- Lack of Reflexivity: Researchers should always acknowledge their own biases. The interpretation of the data should be mindful of how the researcher’s perspective influences the findings.
By following these step-by-step guidelines and applying key techniques, thematic analysis can provide an effective framework for understanding complex qualitative data. It allows researchers to identify themes that provide insights into research questions, supporting qualitative studies in fields such as psychology, education, and qualitative research in sport.
What is the Coding Process in Thematic Analysis?
- Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method that helps researchers identify patterns or themes within data. The coding process is central to this approach, as it allows researchers to organise and interpret qualitative data efficiently.
- Coding data involves breaking down qualitative data into smaller segments and assigning labels (codes) to these segments that represent specific concepts or themes.
Understanding Codes and Themes in Qualitative Research
- Codes: In thematic analysis, codes are short labels or tags that capture a particular piece of data. These codes represent meaningful segments of data and are the foundation for identifying themes in the data.
- Themes: Once codes are identified, they are grouped into themes, which are broader patterns or ideas that provide insight into the research question. Thematic analysis helps to turn raw data into meaningful insights by grouping these codes into themes.
- The analysis of qualitative research data begins by identifying recurring elements or topics, which are then coded for easier categorisation.
How to Code Qualitative Data Efficiently?
- Stage of Data Analysis: Coding happens early in the data analysis process. Researchers begin by transcribing data, reading it repeatedly, and applying initial codes to meaningful segments.
- Organising Codes: As you go through the data, it is important to interpret the data in context. Each segment is then linked to a specific code, allowing researchers to categorise the data into manageable pieces.
- Deeper Analysis: The first round of coding focuses on identifying broad patterns, while later in the analysis, a detailed analysis helps refine the codes and themes, adding more depth to the interpretation.
Ace Your Thesis with Elite Assistance
Make your thesis shine with Elite Thesis Help! Our experienced writers deliver comprehensive, well-researched work to meet all your academic needs. Contact us now and take the first step toward success.
Using a Coding Manual for Thematic Analysis
- Coding Manual: To ensure consistency in coding, researchers often use a coding manual for thematic analysis. This manual defines each code and helps researchers apply it consistently across the data set.
- Thematic Analysis and Content Analysis: While content analysis focuses on counting and categorising data, thematic analysis involves a deeper exploration of the data, identifying broader patterns and meanings.
- The method of qualitative analysis used in thematic analysis requires careful attention to detail, and having a coding manual can help reduce errors and inconsistencies in how codes are applied.
Benefits of Coding in Thematic Analysis
- Thematic analysis can help researchers organise data into meaningful categories, making it easier to interpret the data.
- Coding also assists in identifying recurring patterns and emerging themes in the data, which can then be explored in more depth during the analysis.
- The process of coding and theme development allows for a structured approach to qualitative research methods in mental health, education, and other fields, making the data analysis process more manageable and insightful.
What are Different Approaches to Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a flexible and widely used method in qualitative research. Several approaches to conducting thematic analysis offer different ways to analyse and interpret qualitative data. Each approach has unique features depending on the research question and the data collected.
Reflexive Thematic Analysis Explained
- Reflexive thematic analysis is an approach where the researcher actively engages with the data throughout the entire analysis process. It involves reflecting on how the researcher’s own perspective influences the analysis of qualitative data.
- Unlike other approaches, reflexive thematic analysis does not rely on predefined codes or themes; instead, themes are allowed to emerge from the set of qualitative data through constant reflection and interpretation.
- This method is often used when researchers aim to understand personal or social experiences in a nuanced and interpretive way, making it ideal for phenomenological analysis.
- Thematic analysis is often applied in research aiming to explore deep, subjective meanings within the data, with the researcher’s reflections influencing the interpretation of the findings from thematic analysis.
Comparing Framework Analysis and Thematic Analysis
- Framework analysis and thematic analysis are both popular methods used in qualitative research, but they differ in how data is organised and analysed.
- Framework analysis uses a more structured approach where themes are developed based on a pre-established framework or model. This is more descriptive analysis, focusing on categorising data into specific, predefined themes.
- Thematic analysis, on the other hand, is more flexible and allows themes to emerge organically from the data without relying on an existing framework. Thematic analysis can be used across various types of qualitative research, offering freedom in interpreting data.
- While framework analysis might be ideal for studies with clear questions and predefined goals, thematic analysis is often better suited for research exploring broader, more exploratory questions where themes are not predetermined.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Research
- When deciding between different approaches to conducting thematic analysis, it’s important to consider your research objectives and the type of qualitative paradigm you are using.
- Reflexive thematic analysis is ideal when you want to explore narrative analysis, deeply reflecting on participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Framework analysis is better suited for research that requires systematic organisation of data and where the analysis may need to follow strict guidelines.
- Ultimately, thematic analysis is a method that can adapt to various qualitative approaches, and the right choice depends on whether your study aims for deeper insights into individual experiences (phenomenological analysis) or a more structured, objective analysis of data.
Each approach to thematic analysis offers distinct advantages depending on the scope of your research and the specific goals you have for understanding the data.
How to Use Software for Thematic Analysis?
Using software for thematic analysis can streamline the process of coding, categorising, and interpreting qualitative data. With the right tools, thematic analysis becomes more efficient, especially when working with large sets of qualitative data. Here’s how to leverage software for thematic analysis.
Popular Analysis Software for Qualitative Data
- NVivo: A widely used software tool for qualitative data analysis, NVivo offers features for organising data, coding text, and identifying themes. It allows users to tag and code data throughout the research process, making it easier to analyse the data in relation to the research questions.
- ATLAS.ti: This software is specifically designed for handling complex qualitative data. It facilitates narrative analysis and phenomenological analysis by allowing researchers to annotate, code, and link themes within the data.
- MAXQDA: MAXQDA offers powerful tools for qualitative research, including thematic analysis. It supports both deductive and inductive approaches to thematic analysis, helping researchers identify patterns in a more structured way.
- Dedoose: Ideal for mixed-methods research, Dedoose allows for the coding of qualitative data and its integration with quantitative analysis. Researchers can manage a set of qualitative data and conduct both descriptive analysis and thematic exploration.
Benefits of Using Software in Thematic Analysis
- Efficiency in Data Coding: Software allows for faster coding data, which can be a time-consuming process if done manually. By automatically tagging text segments, software helps researchers focus on deeper analysis and interpretation of the data.
- Organisation of Themes: Software for thematic analysis helps organise themes and codes clearly, making it easier to visualise the relationships between different pieces of data. This can be especially useful when dealing with large datasets, where themes may emerge throughout the data.
- Improved Consistency: Using software ensures consistency in the coding process. A coding manual for thematic analysis can be applied uniformly across the data, reducing human error and increasing the reliability of the findings.
- Ease of Collaboration: Many software tools enable multiple researchers to collaborate on the same project, sharing codes, themes, and notes. This fosters team-based analysis and enhances the richness of the analysis of qualitative data.
Tips for Integrating Software in Your Analysis Process
- Familiarise Yourself with the Software: Before starting, take time to learn the ins and outs of your chosen software. Most tools have extensive tutorials and guides to help users understand the features and interface.
- Import Data Correctly: Ensure that your set of qualitative data is correctly formatted for import into the software. Text data, interviews, or transcripts should be organised in a way that facilitates easy coding and theme development.
- Use Auto-Coding Features Wisely: While software can automatically suggest codes, always review them manually. Thematic analysis requires human insight, and over-reliance on automatic coding may overlook subtle themes in the data.
- Iterative Process: Thematic analysis is an iterative process. Use the software to continuously refine your themes as new patterns emerge throughout the data. This helps maintain flexibility in your analysis and allows for deeper exploration of the data as it evolves.
- Maintain Flexibility: Although software can help manage large datasets, the final interpretation of the data should always involve your own judgement. Thematic analysis is a method that benefits from both technological support and the researcher’s analytical skills.
By integrating software for thematic analysis into your research, you can enhance the efficiency, consistency, and depth of your qualitative research process. Whether you are conducting phenomenological analysis or exploring complex narratives, using software will help you manage and analyse your data with greater ease and precision.
How to Interpret Themes in Thematic Analysis?
Thematic analysis is a powerful method for identifying, analysing, and interpreting patterns within qualitative data. The key to its success lies in effectively interpreting themes that emerge from the data, which requires careful attention and methodological precision.
Developing Themes from Qualitative Data
- Identifying Initial Codes: The first step in thematic analysis is to generate initial codes, which capture important aspects of the qualitative data. These codes are then grouped into potential themes. Developing themes from these codes involves looking for patterns or ideas that are significant in answering the research question.
- Refining Themes: Once potential themes are identified, they should be refined by checking whether they adequately reflect the data and fit within the research question. This process may involve revising themes to ensure they align with the overall research goals.
- Consistency with Research Objectives: Ensure that the themes developed are in relation to the research and directly address the focus of your qualitative study. Thematic analysis can be used throughout the data to ensure that no significant patterns are overlooked.
Analyzing Data Extracts to Identify Themes
- Data Extraction: After coding the data, it is essential to extract relevant segments that exemplify the emerging themes. This involves selecting pieces of text or data extracts that best illustrate the patterns you are seeking to interpret.
- Contextual Interpretation: Interpret the data by considering the context in which the data extract was produced. Understanding the broader context can provide deeper insight into how the theme fits within the overall data set.
- Linking Extracts to Themes: When extracting data, make sure that each extract corresponds to a theme. The connection between the data extract and the identified theme must be clearly defined and justified to ensure validity in the findings from thematic analysis.
Professional Essay Writing Services
Need a standout essay? Elite Thesis Help offers professional writing services tailored to your requirements. Achieve top grades with expertly crafted essays. Reach out today for assistance in achieving your academic goals.
Best Practices for Interpreting Your Findings
- Iterative Process: The process of interpreting themes should be iterative. It is important to continuously return to the data to ensure that the themes still accurately reflect the data and the research question. The researcher’s understanding of the data may evolve throughout the analysis.
- Maintain Reflexivity: Reflexivity is crucial in thematic analysis. Researchers should be aware of their own biases and how these may influence their interpretation of the data. This helps maintain the objectivity of the analysis and ensures that themes are grounded in the data itself rather than preconceived notions.
- Depth of Interpretation: A thorough interpretation should not only describe the themes but also explore their meaning within the context of the research. Descriptive analysis is not enough; deeper analysis is required to understand the underlying significance of each theme.
- Triangulation: If possible, use multiple data sources or methods (such as narrative analysis) to validate the themes. This adds robustness to the findings and reduces the likelihood of bias in theme interpretation.
- Document the Process: At the end of the analysis, it is important to document the steps taken in developing and interpreting the themes. This transparency helps make the thematic analysis process clearer for others and ensures that the interpretation is well-supported by the data.
By following these steps and best practices, you can ensure a rich and valid interpretation of the themes identified through thematic analysis, leading to a deeper understanding of your qualitative data and research question.
